by Coma Historian and Coma News Daily intern Stan Bargmeyer
Otto Lumpkin’s farm was an unlikely setting for one of Coma’s most notorious chapters. It was there, amidst the fields of cabbage and stew tomatoes, a band of militant and disgruntled Buff Orpington chickens led a hasty and tragic armed revolt against Lumpkin and his family.
The birds fashioned swords out of feathers and surprised Lumpkin at dawn as he was scattering feed to the angry mob. Caught completely off guard by the uprising and fearing for his safety, Lumpkin quickly disarmed the nearly two dozen feather-wielding birds and wrangled them back to their coops. The entire ordeal lasted nearly four minutes and left a deep scar in the human-chicken community for years.
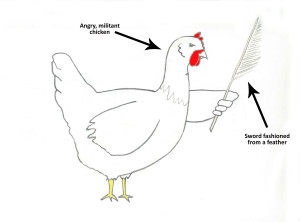
ABOVE: Artist rendering of a chicken clutching an infamous feather sword during the uprising of 1889.
While no serious injuries were reported, Lumpkin noted that several chickens brushed his boots with the feather swords, causing no pain or even slight discomfort.
Local militia were called in following the revolt to help restore order. Several of the birds were sentenced to death and served with cabbage and stewed tomatoes that evening. Others were forced to spend the rest of their lives in captivity.
The ordeal was given the name the “Feather War” by a local reporter who covered the incident for the Coma Daily News in 1889. The tension between humans and chickens continued for several decades, easing slightly during World War I.
Otto Lumpkin is reported to have died in his sleep in 1910 although his death remains controversial to this day as several feathers were found near his bed. Investigators ruled the death from natural causes by many in the community still believe his chickens played a role in his demise.


 Follow
Follow
 comments feed
comments feed